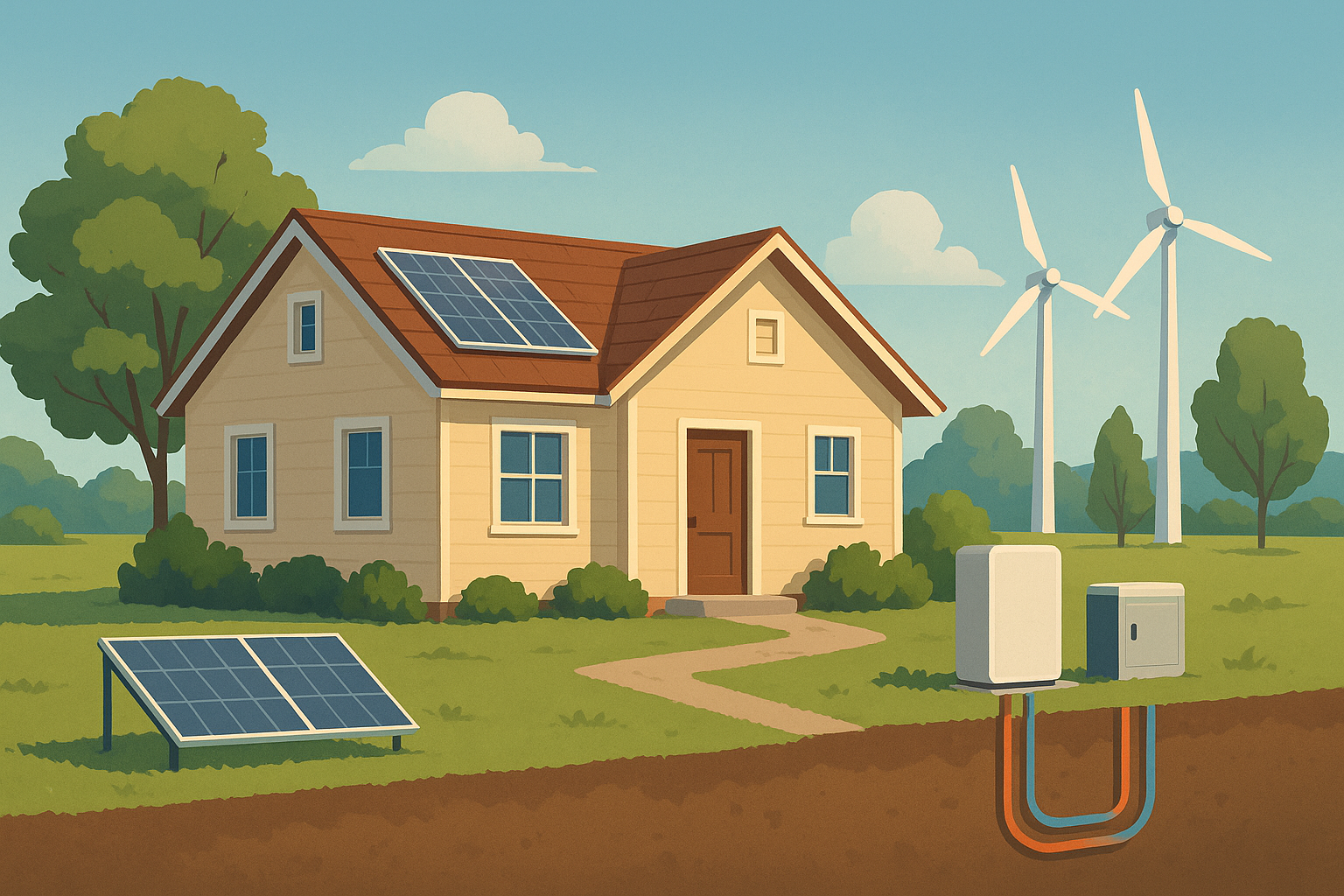
Homeowners across the country are eager to seize control of their energy needs—and for good reason. Solar power often steals the spotlight, and it’s easy to see why. Photovoltaic (PV) panels have become more affordable than ever, and slapping them on your roof feels like a no-brainer. But perhaps it seems that every blog, ad, and neighbor is already on the solar bandwagon. I believe it’s worth recognizing solar’s major role in home energy, then branching out to more niche—but equally compelling—alternatives.
First off, if you haven’t considered solar yet, here’s the gist: panels convert sunlight into electricity, offsetting your utility bills. Pair them with a home battery system (think Tesla Powerwall or LG Chem), and you’ll store excess juice for cloudy days or nighttime use. It seems like a superhero move—clean, quiet, near-silent, and surprisingly low-maintenance.
But guess what? Solar isn’t the only game in town. Homeowners can diversify their on-site energy mix by exploring:
-
Wind Microturbines
Don’t picture towering industrial turbines—think compact, quiet, and roof- or pole-mounted devices. If your property enjoys steady breezes, a small wind turbine can crank out supplemental power. They’re ideal in rural or suburban settings where zoning rules permit. -
Geothermal Heat Pumps
It may sound sci-fi, but geothermal systems tap the earth’s stable underground temperature for heating and cooling. Loops of buried piping circulate a refrigerant, capturing warmth in winter and shedding heat in summer. While upfront installation costs can be higher than traditional HVAC upgrades, geothermal pumps can slash utility bills by up to 70% over their lifetime. -
Solar Thermal Water Heating
Before PV panels hit the scene, solar thermal was already a thing. Flat-plate or evacuated-tube collectors mounted on your roof absorb sunlight to heat a fluid, which then transfers heat to your water tank. You’ll cut natural gas or electric water-heating costs substantially, especially during sunny seasons. -
Biomass Boilers & Stoves
If you live near a source of wood chips, pellets, or other biomass feedstock, consider a biomass boiler or stove. Modern pellet stoves burn compressed wood pellets at high efficiency, offering warmth without the hefty price tag of oil or propane. -
Rainwater Harvesting & Pump Power
While not strictly “electricity,” capturing rainwater for irrigation and dozens of household tasks reduces the energy footprint tied to municipal water. Couple this with a solar- or wind-powered pump, and you’re off-grid in more ways than one. -
Home Batteries & Vehicle-to-Home (V2H)
Even if you go all-in on rooftop solar, peak production doesn’t always align with peak demand. A home battery smooths that gap. And if you own an electric vehicle, some models now allow bidirectional charging—using your car’s battery as a power bank for your home.
Perhaps your best strategy is a hybrid setup: solar panels, a small wind turbine, a geothermal system, and a robust battery backup working in concert. That way, whether the sun’s hidden or a gale blows, your home can generate and store what it needs.
Sure, these systems require research, upfront investment, and occasionally permits. But for motivated homeowners who relish the idea of cutting their bills—and their carbon footprint—there’s a whole toolbox of options beyond panels. It seems that the future of homegrown energy belongs not to single solutions, but to creative combinations tailored to each property’s unique strengths. By embracing more than solar alone, you’ll build resilience, save money, and maybe even spark a little envy in the neighborhood.
